Introduction
Your comfort depends mainly on a complex system hidden within your walls: The HVAC system. This system silently regulates your indoor climate, keeping you cool in summer and warm in winter.
As the famous architect Frank Lloyd Wright once said, “The space within becomes the reality of the building.” Homeowners or anyone interested in creating a comfortable environment should pay attention to the fundamentals of HVAC design services.
This knowledge helps you make informed decisions and empowers you, instilling confidence in optimizing energy efficiency and indoor air quality.
Further, this blog will explain the different types of HVAC systems and how they operate, providing valuable knowledge you can easily apply in real-world situations.
What is an HVAC System?
An HVAC system is the abbreviation for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. It uses components that synchronize indoor climate by controlling the building’s temperature, humidity, and air quality.
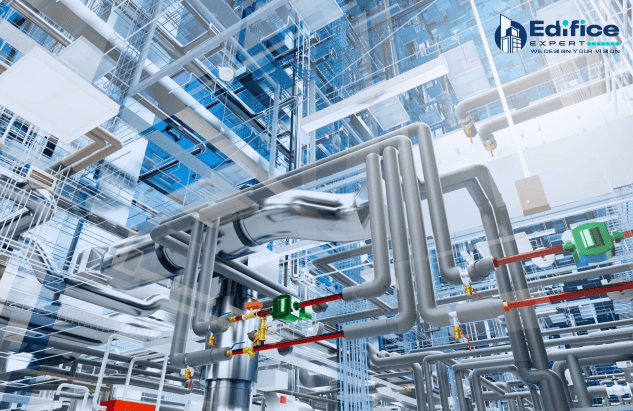
In addition to basic HVAC knowledge, incorporating BIM in HVAC design has changed how these systems work and execute, allowing for highly precise and efficient installations. This is especially needed when integrating HVAC and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) systems, guaranteeing a coordinated and optimized building infrastructure.
83% of consumers identified HVAC systems as a priority, with nearly 38% prioritizing system reliability when selecting HVAC equipment.
HVAC System Basics Components
1) Thermostat
The thermostat sets the balance between the temperature and operation of the HVAC system.
2) Furnace/Heat Pump
A furnace or heat Pump offers heating (furnace) or extracts heat from the environment (heat pump).
3) Air Conditioner
Air Conditioner quickly cools down indoor air by removing heat and moisture.
4) Ductwork
Ductwork distributes heated or cooled air within the entire building.
5) Vents
Vents regulate the air temperature and humidity in your home.
6) Filters
Filters in the system remove contaminants from the air.
7) Blower Motor
Blower Motor circulates air in the system.
8) Condenser Coil
Condenser Coil releases heat from the refrigerant.
9) Evaporator Coil
Evaporator Coil absorbs heat from indoor air.
10) Humidifier/Dehumidifier
Humidifier/Dehumidifier controls the levels of humidity.
11) Air Handler Unit
The air-handler unit combines heating, cooling, and ventilation components.
12) Controls
Controls regulate the operation of the HVAC system.
Types of HVAC systems
Understanding the different types of HVAC systems is very important for making informed decisions about energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and occupant well-being.
1) Split Systems
This type of HVAC is commonly used with essential HVAC components like separate indoor and outdoor units. The indoor unit generally contains the evaporator coil and air handler, while the outdoor unit houses the compressor and condenser coil.
Split systems are mainly used for residential and small commercial buildings.
2) Hybrid Systems
These systems are similar to split systems but incorporate HVAC components and function as heat pumps that can switch between electricity and fossil fuels to improve energy use.
Hybrid systems, on the other side, are efficient in varying climates.
3) Duct-Free Systems
This system, known as a mini-split system, is perfect for buildings without ductwork.
This type of system consists of an outdoor unit connected to one or more indoor units offering zoned heating and cooling.
4) Packaged Systems
This system’s HVAC mechanical system has all components in a single outdoor unit, often installed on rooftops.
This system is commonly used in commercial buildings and can provide heating and cooling.
5) Geothermal HVAC Systems
This system uses the earth’s stable underground temperature to heat and cool buildings.
These systems are also highly energy-efficient and environment-friendly, requiring a heavy upfront investment.
How do HVAC systems work?
Let us understand how HVAC Systems work step by step,
1) Heating
Furnaces: These burn fuel (such as natural gas or oil) to produce heat. The heat is then dispensed through the building through a network of ducts.
Heat Pumps: With heat pumps, heat will be shifted from the outside air into the building or space. This process can also be done in the reverse motion to cool the building.
Boilers: With boilers, the heated water will be circulated through radiators to warm the building or space.
2) Ventilation
Natural Ventilation: This method typically depends on openings like windows and vents to let the fresh air pass to stale air that will leave the windows.
Mechanical Ventilation: This method uses fans and duct systems to control airflow. It also includes exhaust ventilation and removes stale air from kitchens and bathrooms.
Supply Ventilation: Now, this step brings fresh air into the building, which can then be filtered and conditioned.
Balanced Ventilation: This step will combine exhaust and supply systems to maintain a balanced airflow.
3) Air Conditioning (Cooling)
Central Air Conditioners: This step uses a refrigeration cycle to cool air distributed through ducts.
Split Systems: These systems have an outdoor unit that dissipates heat and an indoor unit that cools the air. Here, mechanical engineering design services are essential in optimizing these systems, ensuring they are efficient and tailored to specific building needs.
Window Units and Portable ACs: These compact units cool a single room or area.
How much does a new HVAC system design cost?
The cost of a new HVAC system design is purely dependent upon factors such as the complexity of the MEP design for a building, the system’s complexity, and the building’s location and size.
But again, on average, residential building homeowners can expect to pay between $5,000 and $12,000 for a new HVAC system.
In commercial buildings, the design of an HVAC system ranges from $25 to $60 per square foot, depending on the unit size and brand.
Benefits of using BIM in HVAC Design
BIM will allow smooth integration of HVAC systems with other building components, minimizing clashes and rework.
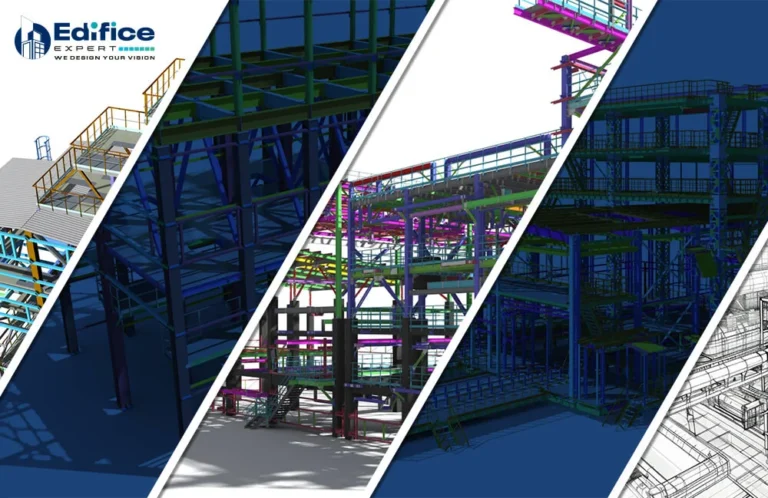
3D models offer a clear visual representation of HVAC systems, aiding design decisions and stakeholder communication.
BIM tools allow energy analysis and optimization to provide more sustainable and cost-effective HVAC systems.
By aligning the design and construction process, BIM leverages effective collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors.
Potential issues can be easily identified using 3D modeling services, and optimized design choices help minimize construction costs.
Early identification of problems through clash detection and analysis reduces project risks.
BIM enables thorough quality checks and ensures compliance with design specifications.
Choosing the Right HVAC Outsourcing Services
Edifice Expert is the right choice when it comes to outsourcing HVAC services. They offer detailed 3D BIM Modeling Services that are highly accurate and collaborative among stakeholders. Their expertise in MEP design ensures smooth integration of HVAC systems within your building, reducing errors and maximizing efficiency
“Investing in a good HVAC system means investing in the well-being and productivity of the people who use the space.”
By outsourcing to Edifice Expert, you will also benefit from advanced technology and skilled professionals, resulting in cost savings, improved project timelines, and excellent quality at its best!
Conclusion
By understanding how these systems work, including heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, individuals can make informed decisions regarding installation, maintenance, and energy efficiency that will ultimately level the comfort and sustainability of their living and working environments.